interview - JS regular function 常用函数实现
native polyfill / rewrite (browser + Node.js)
String
String.trim()
str => str.replace(/(^\s+)|(\s+$)/g, "")
Array
// Array common verify args
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(fn) != "[object Function]") {
throw new TypeError(fn + " is not a function")
}
map
Array.prototype.map = function(fn, thisArg) {
// verify fn, this
var arr = this,
res = [],
T = thisArg || void 0
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
res.push(fn.call(T, arr[i], i, arr))
}
return res
}
reduce
// if reduceRight, amend i
Array.prototype.reduce = function(fn, initValue) {
const arr = this
const len = arr.length
let r = arr[0]
let i = 0
if (typeof initValue !== "undefined") {
r = initValue
i--
}
while (++i < len) {
r = fn(r, arr[i], i, arr)
}
return r
}
filter
Array.prototype.filter = function(fn, thisArg) {
const arr = this
const len = arr.length
const res = []
let i = -1
while (++i < len) {
const r = fn.call(thisArg, arr[i], i, arr)
if (r) res.push(arr[i])
}
return res
}
flat / flatten
flat = arr => {
// if allow reduce
return arr.reduce((acc, cur) => {
if (Array.isArray(cur)) acc.push(...flat(cur))
else acc.push(cur)
return acc
}, [])
// not allowed
var res = []
arr.forEach(e => {
if (Array.isArray(e)) res.push(...flat(e))
else res.push(e)
})
return res
}
Promise
Promise polyfill
Promise 化 ajax
function myXHR(method, url, data) {
var requset = new XMLHttpRequest()
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
requset.onreadystatechange = function() {
if (requset.readyState === 4) {
if (requset.status === 200) resolve(requset.responseText)
else reject(requset.status)
}
}
requset.open(method, url)
requset.send(data)
})
}
var p = myXHR("GET", "url")
p.then(responseText => {
console.log(responseText)
}).catch(status => {
console.log(new Error(status))
})
Iterator (TODO)
forEach
/**
* @param {Object|Array} obj The object to iterate
* @param {Function} fn The callback to invoke for each item
*/
function forEach(obj, fn) {
// Don't bother if no value provided
// 判断 null 和 undefined 直接返回
if (obj === null || typeof obj === "undefined") return
// Force an array if not already something iterable
// 如果不是对象,放在数组里。
if (typeof obj !== "object") {
obj = [obj]
}
// 是数组 则用for 循环,调用 fn 函数。参数类似 Array.prototype.forEach 的前三个参数。
if (Array.isArray(obj)) {
// Iterate over array values
for (var i = 0, l = obj.length; i < l; i++) {
fn.call(null, obj[i], i, obj)
}
} else {
// Iterate over object keys
// 用 for in 遍历对象,但 for in 会遍历原型链上可遍历的属性。
// 所以用 hasOwnProperty 来过滤自身属性了。
// 其实也可以用Object.keys来遍历,它不遍历原型链上可遍历的属性。
// for (var key in obj) {
// if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
// fn.call(null, obj[key], key, obj);
// }
// }
// better
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => {
fn.call(void 0, obj[key], key, obj)
})
}
}
Object
new
function _new(Fn, ...args) {
// 1. 创建新对象
let obj = {}
// 2. 空对象的原型指向函数的面试
obj.__proto__ = Fn.prototype
// 3. 执行构造函数, 添加属性和方法
let res = Fn.apply(obj, args)
// 4. return
if (res && (typeof res === "object" || typeof res === "function")) return res
return obj
}
// test
function Super(age) {
this.age = age
return { age: 2 }
}
let a = new Super(10)
console.log(a.age) // 2
create()
if (typeof Object.create !== "function") {
Object.create = function(proto, propertiesObject) {
if (typeof proto !== "object" && typeof proto !== "function") {
throw new TypeError("Object prototype may only be an Object: " + proto)
} else if (proto === null) {
throw new Error(
"This browser's implementation of Object.create is a shim and doesn't support 'null' as the first argument."
)
}
if (typeof propertiesObject != "undefined")
throw new Error(
"This browser's implementation of Object.create is a shim and doesn't support a second argument."
)
function F() {}
F.prototype = proto
return new F()
}
}
Function
apply 参考
function gThis() {
return this
}
function gFn(length) {
var code = "return arguments[0][arguments[1]]("
for (var i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (i > 0) code += ","
code += "arguments[2][" + i + "]"
}
code += ")"
return code
}
function gArguments(args) {
let arg = []
for (let i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
arg[i] = "args[" + i + "]"
}
return arg
}
Function.prototype.apply = function(thisArg, args) {
// 1.如果 `IsCallable(func)` 是 `false`, 则抛出一个 `TypeError` 异常。
if (typeof this !== "function")
throw new TypeError(this + " is not a function")
if (typeof args === "undefined" || args === null) args = []
if (!thisArg) thisArg = gThis()
thisArg = new Object(thisArg)
var __fn__ = Math.random()
// const fn = Symbol('fn') // ES6
while (thisArg[__fn__]) {
__fn__ = Math.random()
}
thisArg[__fn__] = this
// new Function()
var res = new Function(gFn(args.length))(thisArg, __fn__, args)
// ES6
// const res = thisArg[__fn__](...args)
// eval()
// var res = eval('thisArg[__fn__]('+gArguments(args)+')')
delete thisArg[__fn__] // ES6: Reflect.deleteProperty(thisArg, 'fn')
return res
}
call
Function.prototype.call = function() {
// apply same verification
var thisArg = arguments[0]
var args = Array.prototype.slice(arguments, 1)
return this.apply(thisArg, args)
}
Note
call = fn.call 引发的 this 指向错误
const arrayLike = { length: 0 }
const call = [].push.call // typeof call "function"
call(arrayLike, 1) // call is not a function
// because "this" inside `call` points to global "this", thus there is no `call` on window/global/globalThis.
bind
see full in MDN
Function.prototype.bind = function(thisArg) {
// verify this is Funtion
var T = thisArg || void 0,
fn = this
var slice = Array.prototype.slice
var args = slice.call(arguments, 1) || []
// simplify
// return function() {
// var _args=args.concat(slice.call(arguments))
// return fn.apply(T, _args)
// }
// full
var fNOP = function() {}
var fbound = function() {
var _args = args.concat(slice.call(arguments))
return fn.apply(fNOP.prototype.isPrototypeOf(this) ? this : T, _args)
}
if (this.prototype) fNOP.prototype = fn.prototype // assign fn's prototype to fNOP
fbound.prototype = new fNOP()
return fbound
}
继承
原型链
function F() {}
var f = new F()
// 构造器
F.prototype.constructor === F // true
F.__proto__ === Function.prototype // true
Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype // true
Object.prototype.__proto__ === null // true
// 实例
f.__proto__ === F.prototype // true
F.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype // true
Object.prototype.__proto__ === null // true
class
- 类属性使用
this绑定 - 类方法使用
prototype对象来绑定 - 为了继承属性, 使用
call函数来传递 this (类似 super) - 为了继承方法,使用
Object.create连接父和子的原型 - 始终将子类构造函数设置为自身,以获得其对象的正确类型 (constructor)
// 1.
function Animal(name, type) {
this.name = name
this.type = type
}
// 2.
Animal.prototype.shout = function() {
return this.name + " shout"
}
// 3.
function Dog(name, type) {
Animal.call(this, name, type)
this.sound = "bow"
}
// 4. Link prototype chains to inherit parent class functions
Dog.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype)
// 5. target the constructor to itself
Dog.prototype.constructor = Dog
// 原型链上的属性
function Person() {}
Person.prototype.friend = []
Person.prototype.name = ""
var a = new Person()
a.friend[0] = "Ana"
a.name = "Bob"
var b = new Person()
console.log(b.friend) // Ana
console.log(b.name) // ''
extends
function _extends(Child, Parent) {
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype) // Object.create
Child.prototype.constructor = Child // = Child.prototype.__proto__ = Parent.prototype;
Child.__proto__ = Parent // = Object.setPrototypeOf(Child, Parent);
}
functional programming / utils / helpers (lodash, underscore, ramda)
curry 柯里
!!! curry 帮助创建 偏函数 Partial function
curry = (fn, ...args) =>
args.length >= fn.length
? fn(...args)
: (...args2) => curry(fn, ...args, ...args2)
// ES5 curry
curry = function(fn) {
if (typeof fn !== "function") throw new TypeError("")
var slice = Array.prototype.slice
var args1 = slice.call(arguments, 1)
return args1.length >= fn.length
? fn.apply(void 0, args1)
: function() {
var args2 = [fn].concat(args1, slice.call(arguments))
return curry.apply(void 0, args2)
}
}
// 调用
const foo = (a, b, c) => a * b * c
curry(foo)(2, 3, 4) // -> 24
curry(foo, 2)(3, 4) // -> 24
curry(foo, 2, 3)(4) // -> 24
curry(foo, 2, 3, 4) // -> 24
// e.g. infinite sum, hint: arguments.length
const sum = (a, b = 0) => {
if (arguments.length === 0) return b
return n => {
let res = a + b
return sum(n, res)
}
}
console.log(sum(100, 200)(300)(400)())
compose & pipe/lodash.flow
compose = (...fns) => (...args) => {
let i = fns.length - 1
let res = fns[i].apply(this, args)
while (i--) res = fns[i].call(this, res)
return res
}
pipe = (...fns) => (...args) => {
let i = 0
let res = fns[i].apply(this, args)
while (++i < fns.length) res = fns[i].call(this, res)
return res
}
Functor 函子 (homomorphisms between categories)
Functor 是类别之间保留结构的转换。 这是一种将对象从一个类别映射到另一类别的对象,同时又保留对象之间的箭头的一种方法 - 将其视为类别同构。
Endofunctor 是从一个类别回到同一类别的函子。
A functor is a structure-preserving transformation between categories.
An endofunctor is a functor from one category back to the same category.
简单函子
var a = Functor.of(1)
.add(4)
.multiply(4) // { val:20 }
Functor.of(1)
.map(add4)
.map(multiply4) // { val: 20 }
a == 20 // true
function Functor(val) {
this.val = val
}
Functor.of = val => new Functor(val)
Functor.prototype.map = function(f) {
return Functor.of(f(this.val))
}
Functor.prototype.add = function(n) {
return Functor.of(this.val + n)
}
Functor.prototype.multiply = function(n) {
return Functor.of(this.val * n)
}
Functor.prototype.toString = function() {
return this.val
}
Maybe, 增加空值判断
Either 函子是指内部有分别有左值和右值, 优先使用右值
Maybe.prototype.map = function(f) {
return this.val ? Maybe.of(f(this.val)) : Maybe.of(null)
}
function Either(left, right) {
this.left = left
this.right = right
}
Either.prototype.map = function(f) {
return this.right
? Either.of(this.left, f(this.right))
: Either.of(f(this.left), this.right)
}
Either.of = function(left, right) {
return new Either(left, right)
}
TODO
Monad, 能够将多层嵌套函子解除的函子, 我们往函子传入的值不仅仅可以是普通的数据类型,也可以是其它函子,当往函子内部传其它函子的时候,则会出现套娃函子。
// 新增 join, flatMap,通过 flatMap 我们能够在每一次传入函子的时候都将嵌套解除。
Monad.prototype.join = function() {
return this.val
}
Monad.prototype.flatMap = function(f) {
return this.map(f).join()
}
const nested = Monad.of(Monad.of("nested"))
console.log(
Monad.of(nested)
.flatMap(Monad.of)
.flatMap(Monad.of)
)
debounce 防抖
!!! underscore.debounce
不管触发了多少次回调,只认最后一次
// Returns a function, that, as long as it continues to be invoked, will not
// be triggered. The function will be called after it stops being called for
// N milliseconds. If `immediate` is passed, trigger the function on the
// leading edge, instead of the trailing.
function debounce(func, wait, immediate) {
var timeout
return function() {
var context = this,
args = arguments
var later = function() {
timeout = null
if (!immediate) func.apply(context, args)
}
var callNow = immediate && !timeout
clearTimeout(timeout)
timeout = setTimeout(later, wait)
if (callNow) func.apply(context, args)
}
}
throttle 节流
naive.throttle
var throttle = function(fn, wait) {
var last = 0
return function() {
var curr = +new Date()
if (curr - last > wait || !last) {
fn.apply(this, arguments)
last = curr
}
}
}
debounced throttle: 定时器 + 时间戳, 第一次和最后一次都会触发
function throttle(fn, wait) {
let pre = 0
let timer = null
return function(...args) {
let now = Date.now()
if (now - pre > wait) {
clearTimeout(timer)
timer = null
pre = now
fn.apply(this, args)
} else if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
fn.apply(this, args)
}, wait)
}
}
}
underscore.throttle
在某段时间内,不管触发了多少次回调,都只认第一次,并在计时结束时给予响应。
// Returns a function, that, when invoked, will only be triggered at most once
// during a given window of time. Normally, the throttled function will run
// as much as it can, without ever going more than once per `wait` duration;
// but if you'd like to disable the execution on the leading edge, pass
// `{leading: false}`. To disable execution on the trailing edge, ditto.
function(func, wait, options) {
var timeout, context, args, result;
var previous = 0;
if (!options) options = {};
var later = function() {
previous = options.leading === false ? 0 : Date.now();
timeout = null;
result = func.apply(context, args);
if (!timeout) context = args = null;
};
var throttled = function() {
var now = Date.now();
if (!previous && options.leading === false) previous = now;
var remaining = wait - (now - previous);
context = this;
args = arguments;
if (remaining <= 0 || remaining > wait) {
if (timeout) {
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = null;
}
previous = now;
result = func.apply(context, args);
if (!timeout) context = args = null;
} else if (!timeout && options.trailing !== false) {
timeout = setTimeout(later, remaining);
}
return result;
};
throttled.cancel = function() {
clearTimeout(timeout);
previous = 0;
timeout = context = args = null;
};
return throttled;
};
native extension
Array.disorder
数组乱序: 从最后一个元素始 随机选一个元素,交换
Array.prototype.disorder = function() {
// verify Array.isArray(this)
var arr = this,
l = arr.length,
i = l
while (--i >= 0) {
const rand = (l * Math.random()) | 0
let tmp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[rand]
arr[rand] = tmp
}
return arr
}
EventEmitter (Node.js)
同时也是 PubSub 和 Subject 的实现
on对应subscribeoff对应unsubscribepublish对应emit
Observer 相当于 每个 listener 单独实现
参考知乎链接
观察者模式
它定义了对象间的一种一对多的关系,让多个观察者对象同时监听某一个主题对象,当一个对象发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都将得到通知。
观察者模式在前端开发中非常常用, 我们经常用的事件就是观察者模式的一种体现,它对我们解耦模块,开发基于消息的业务起着非常重要的作用。
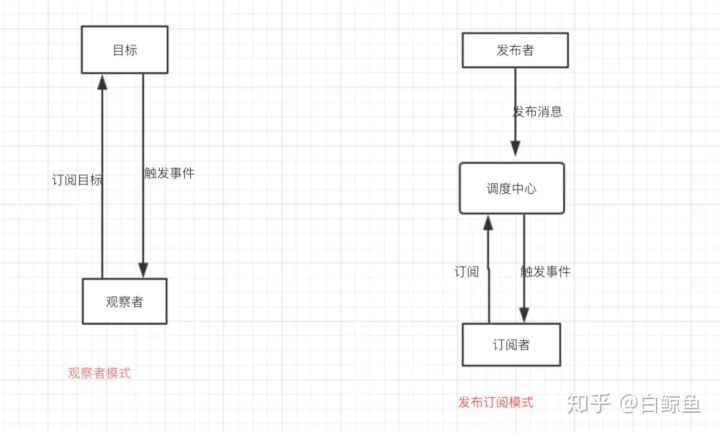 从图中可以看出,观察者模式中观察者和目标直接进行交互,而发布订阅模式中统一由调度中心进行处理,订阅者和发布者互不干扰。
从图中可以看出,观察者模式中观察者和目标直接进行交互,而发布订阅模式中统一由调度中心进行处理,订阅者和发布者互不干扰。
观察者模式的订阅者与发布者之间是存在依赖的,而发布/订阅模式则不会。
发布 / 订阅模式优势在于, 这样一方面实现了解耦,还有就是可以实现更细粒度的一些控制。比如发布者发布了很多消息,但是不想所有的订阅者都接收到,就可以在调度中心做一些处理,类似于权限控制之类的。还可以做一些节流操作。
// notice: chain functions: on, emit, off, once
class EventEmitter {
constructor() {
this.listeners = {}
// this.maxLength = 10
}
on(type, cb, prepend = false) {
// addListener() + prependListener()
const fns = this.listeners[type] || (this.listeners[type] = [])
if (Array.isArray(fns) && !fns.includes(cb) && typeof cb === "function") {
if (prepend) fns.unshift(cb)
else fns.push(cb)
}
return this
}
emit(type, ...args) {
const fns = this.listeners[type]
if (Array.isArray(fns)) {
fns.forEach(cb => cb(...args))
}
return this
}
off(type, cb) {
// removeListener() + removeAllListeners()
const fns = this.listeners[type]
if (Array.isArray(fns)) {
if (typeof cb === "function") {
const i = fns.indexOf(cb)
if (i > -1) fns.splice(i, 1)
} else fns.length = 0
}
return this
}
once(type, cb) {
const self = this
function fn(...args) {
cb(...args)
self.off(type, fn)
}
this.on(type, fn)
return this
}
// setMaxListeners(n) { this.maxLength = n }
// listeners(type) { return this.listeners[type] || [] }
// EventEmitter.prototype.on = EventEmitter.prototype.addListener
// EventEmitter.prototype.off = EventEmitter.prototype.removeListener
// 特殊事件名:
// 'newListener': 如监听, 每次新加事件时会触发
// 'removeListener': 如监听, 每次删除事件时会触发
// nodejs EventEmitter 捕获异常, 使用 domain 模块
}
math calculation
BigInt Sum 大数相加
/**
* @param {string} a
* @param {string} b
* @return {string}
*/
function sum(a, b) {
var l = Math.max(a.length, b.length)
a = a.padStart(l, 0)
b = b.padStart(l, 0)
var i = l,
carry = 0,
r = "",
tmp
while (--i > -1) {
tmp = Number(a[i]) + Number(b[i]) + carry
if (tmp > 9) {
tmp -= 10
carry = 1
} else carry = 0
r = tmp + r
}
return carry === 1 ? "1" + r : r
}
fibonacci 斐波那契数列
function fibonacci(n) {
var a = 0,
b = 1
while (n-- > 0) [a, b] = [b, a + b]
return a
}
data structure
TODO Complete Binary Search Tree
TODO MaxHeap / PriorityQueue
refer to google closure
Trie Tree 字典树
function TrieNode(key) {
this.key=key;
this.children=[]
}
function Trie(root) {
this.root=root
}
Trie.prototype = {
// 插入单词
insertData:(stringData)=>void,
insert:(stringData,node)=>void,
// 查找单词
search:(queryData)=>boolean,
searchNext:(node,stringData)=>boolean, // 递归
// 删除单词
delete:(stringData)=>this,
delNext:(parent, index, stringData, delStr)=>boolean, // 递归
// 打印树上的所有单词
printData:()=>void,
printHelper:(node, data)=>void // 递归
}
browser related
requestAnimationFrame
与 setTimeout 相比, requestAnimationFrame 最大的优势是 由系统来决定 回调函数的执行时机. 具体一点讲, 如果屏幕刷新率是 60Hz, 那么回调函数就每 16.7ms 被执行一次, 如果刷新率是 75Hz, 那么这个时间间隔就变成了 1000/75=13.3ms. 它能保证回调函数在屏幕每一次的刷新间隔中只被执行一次,这样就不会丢帧.
rAF 执行过程
- 读取
document.hidden, 页面可见时才执行 - 清空上一轮函数
handlerId会和动画函数callback, 进入动画帧请求回调函数列- 浏览器遍历动画帧请求回调列表, 根据
handlerId大小依次执行相应动画函数
(function () {
var lastTime = 0;
var vs = ['ms', 'moz', 'webkit', 'o'];
for (var i=0; i<vs.length && !window.requestAnimationFrame; ++i) {
window.requestAnimationFrame = window[vs[i]+'RequestAnimationFrame'];
window.cancelAnimationFrame = window[vs[i]+'CancelAnimationFrame']
|| window[vs[i]+'CancelRequestAnimationFrame'];
}
// iOS6 is buggy
if (/iP(ad|hone|od).*OS 6/.test(window.navigator.userAgent ||
!window.requestAnimationFrame || !window.cancelAnimationFrame) {
window.requestAnimationFrame = function (callback) {
var now = window.performance ? performance.now() : +new Date
var nextTime = Math.max(now, lastTime+16)
return setTimeout(function () { // setTimeoutId as handlerId
callback(lastTime=nextTime)
}, nextTime-now);
};
window.cancelAnimationFrame = clearTimeout
};
}());
// test
var progress = 0;
function render() {
if (++progress<100) window.requestAnimationFrame(render) // handlerId
}
window.requestAnimationFrame(render); //第一帧渲染
delegate 事件委托
// 监听父元素, 通过 `e.target.nodeName` 限定委托元素 e.target
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() {
let app = document.getElementById("parent")
app.addEventListener("click", function(e) {
if (e.target && e.target.nodeName === "LI") {
let item = e.target
alert("you clicked on item: " + item.innerHTML)
}
})
})
图片懒加载
监听图片高度
用一个其他属性存储真正的图片地址:
<img
src="loading.gif"
data-src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2015/09/09/16/05/forest-931706_1280.jpg"
alt=""
/>
<img
src="loading.gif"
data-src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2014/08/01/00/08/pier-407252_1280.jpg"
alt=""
/>
通过图片offsetTop和window的innerHeight,scrollTop判断图片是否位于可视区域。
// 用自执行函数包裹
var imgs = document.getElementsByTagName("img")
var n = 0 //存储图片加载到的位置,避免每次都从第一张图片开始遍历
lazyload() //页面载入完毕加载可是区域内的图片
// 节流函数,保证每200ms触发一次
function throttle(fn, time) {
let timer
return function(...args) {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null
fn(...args)
}, time)
}
}
}
// if needed, removeListener in the end
var throttled = throttle(lazyload, 200)
window.addEventListener("scroll", throttled)
function lazyload() {
//监听页面滚动事件
var seeHeight = window.innerHeight //可见区域高度
// document.documentElement 是整个 <html></html>
var scrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop
//滚动条距离顶部高度
for (var i = n; i < img.length; i++) {
// or use
// img[i].getBoundingClientRect().top <= window.innerHeight
if (img[i].offsetTop < seeHeight + scrollTop) {
if (img[i].getAttribute("src") == "loading.gif") {
img[i].src = img[i].getAttribute("data-src")
}
n = i + 1
}
}
}
IntersectionObserver (异步)
!!!
IntersectionObserver 接口 (从属于 Intersection Observer API) 提供了一种异步观察目标元素与其祖先元素或顶级文档视窗(viewport)交叉状态的方法。祖先元素与视窗(viewport)被称为根(root)。
Intersection Observer可以不用监听scroll事件,做到元素一可见便调用回调,在回调里面我们来判断元素是否可见。
if (IntersectionObserver) {
let lazyImageObserver = new IntersectionObserver((entries, observer) => {
entries.forEach((entry, index) => {
let lazyImage = entry.target
// 如果元素可见
if (entry.intersectionRatio > 0) {
if (lazyImage.getAttribute("src") == "loading.gif") {
lazyImage.src = lazyImage.getAttribute("data-src")
}
lazyImageObserver.unobserve(lazyImage)
}
})
})
for (let i = 0; i < img.length; i++) {
lazyImageObserver.observe(img[i])
}
}