interview - React
Concept 基本原理
react.js is a library for UI view layer via manipulating virtual dom; react-dom and react-native are the implementation for the platforms.
纯函数
- 相同的输入产生相同的输出(不能在内部使用 Math.random,Date.now 这些方法影响输出)
- 输出不能和输入值以外的任何东西有关(不能调用 API 获得其他数据)
- 函数内部不能影响函数外部的任何东西(不能直接改变传入的引用变量),即不会突变
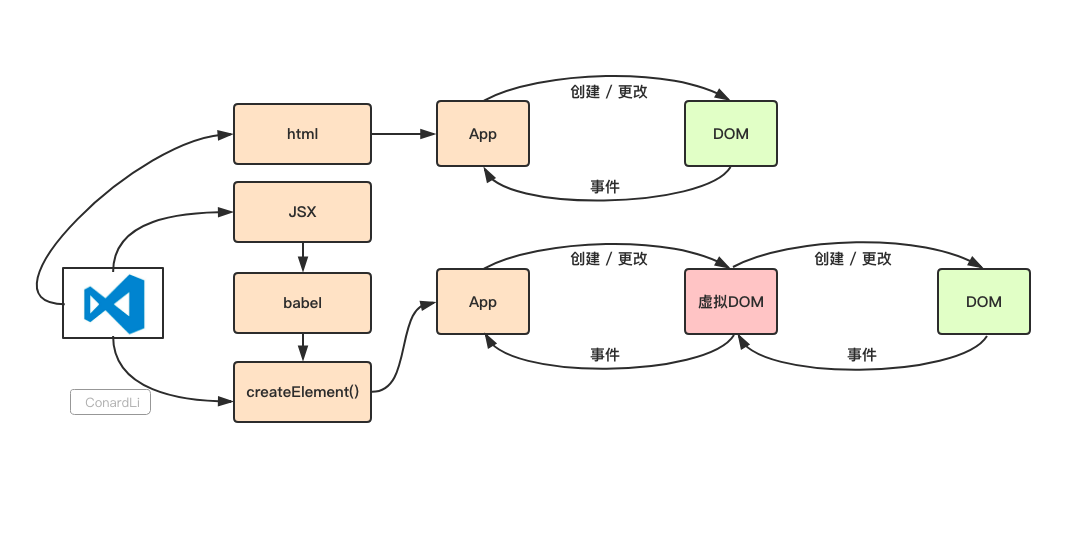
Virtual DOM
通过类似 html tag 的 JSX, 使用 babel 创建 vdom, 根据虚拟 dom 渲染 dom tree, 每次更新 diff vdom, 然后重新渲染.
参考 !!!
KEY babel transform
{
"plugins": [
[
"transform-react-jsx",
{
"pragma": "React.createElement"
}
]
]
}
createElement(), 数据结构如下
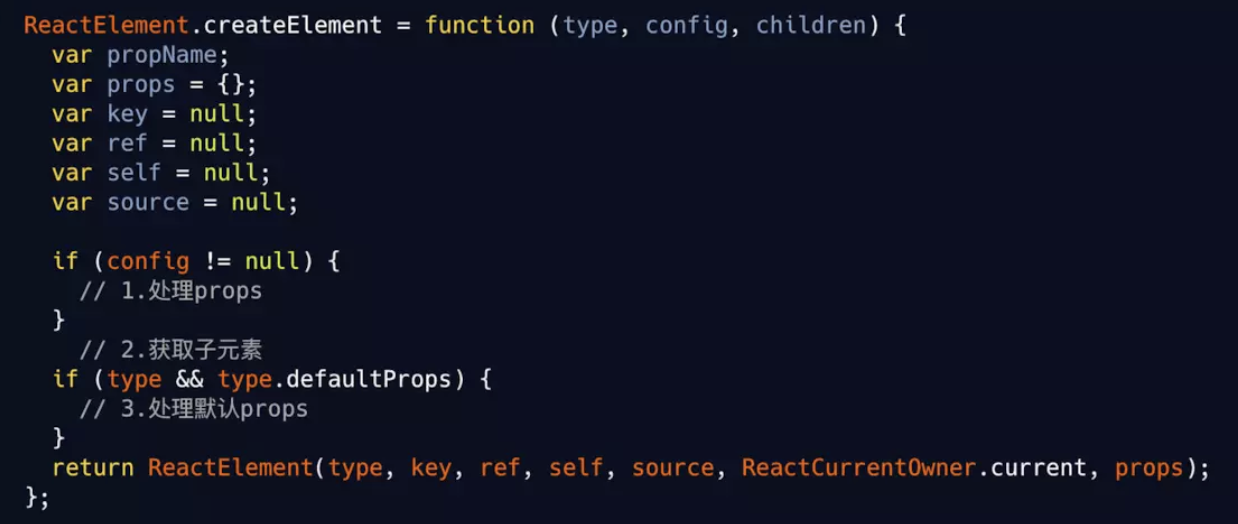
// ReactElement
{
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,
type,
key,
ref,
props,
_owner: owner,
}
React.Component
function Component(props, context, updater) {
this.props = props
this.context = context
// If a component has string refs, we will assign a different object later.
this.refs = emptyObject
// We initialize the default updater but the real one gets injected by the
// renderer.
this.updater = updater || ReactNoopUpdateQueue
}
Component.prototype.isReactComponent = {}
Component.prototype.setState = function(partialState, callback) {
this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState, callback, "setState")
}
Component.prototype.forceUpdate = function(callback) {
this.updater.enqueueForceUpdate(this, callback, "forceUpdate")
}
ReactDOM
const ReactDOM: Object = {
createPortal,
findDOMNode(
componentOrElement: Element | ?React$Component<any, any>
): null | Element | Text {},
hydrate(element: React$Node, container: DOMContainer, callback: ?Function) {
return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
null,
element,
container,
true,
callback
)
},
render(
element: React$Element<any>,
container: DOMContainer,
callback: ?Function
) {
return legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
null,
element,
container,
false,
callback
)
}
// ...
}
LifeCycle
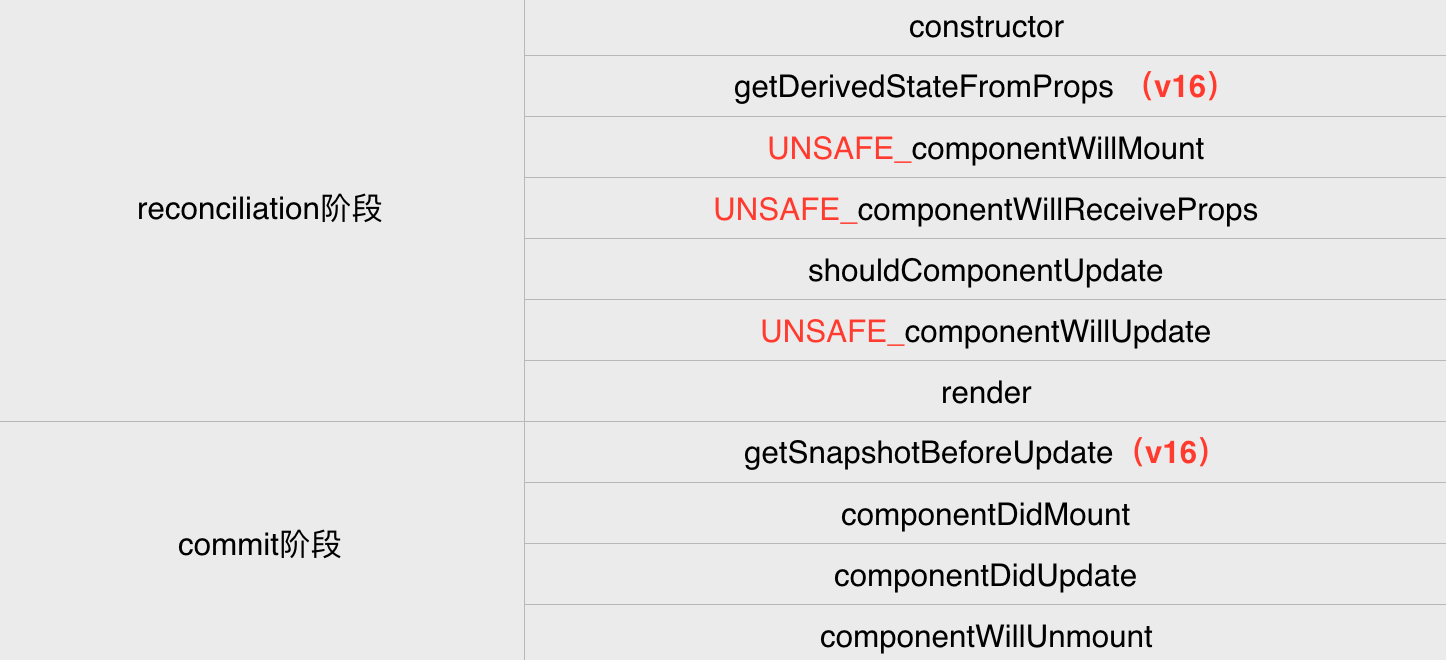
setState()
async, batch, trigger update & rerender (if shouldComponentUpdate is not optimized)
在实际开发中,setState 的表现有时会不同于理想情况:
- 在 mount 流程中调用 setState。
- 在 setTimeout/Promise 回调中调用 setState。 在第一种情况下,不会进入 update 流程,队列在 mount 时合并修改并 render。
在第二种情况下,setState 将不会进行队列的批更新,而是直接触发一次 update 流程。
这是由于 setState 的两种更新机制导致的,只有在 批量更新模式 中,才会是 “异步” 的。
直接传递对象的 setState({ ... }, () => {}) 会被合并成一次
使用函数传递 setState(prev => ({}), () => {}) 不会被合并
因此
componentDidMount() {
this.setState({ index: this.state.index + 1 }, () => {
console.log(this.state.index);
})
this.setState({ index: this.state.index + 1 }, () => {
console.log(this.state.index);
})
// 1, 1
}
componentDidMount() {
this.setState(preState => ({ index: preState.index + 1 }), () => {
console.log(this.state.index);
})
this.setState(preState => ({ index: preState.index + 1 }), () => {
console.log(this.state.index);
})
// 2, 2
}
Diff VDOM ( O(n^3) -> O(n) )
参考知乎 开销最大, 可做优化最多, 三条基本策略/依据:
- WebUI 中 DOM 节点跨节点的操作特别少,可以忽略不计。
- 拥有相同类的组件会拥有相似的 DOM 结构。拥有不同类的组件会生成不同的 DOM 结构。
- 同一层级的子节点,可以根据唯一的 ID 来区分。
具体方法:
Tree Diff: 对树进行分层比较,只对比两棵树同级别的节点。跨层级移动节点,将会导致节点删除,重新插入,无法复用。Component Diff: 对组件进行类比较,类相同的递归 diff 子节点,类不同的销毁重建。diff 对同一层级的子节点进行处理时,会根据 key 进行简要的复用。两棵树中存在相同 key 的节点时,只会移动节点。可通过shouldComponentUpdate()优化Element Diff: 对比同一层级子节点时, 以新树的第一个子节点作为起点遍历新树,寻找旧树中与之相同的节点。存在则移动位置, 不存在则新建一个子节点. 通过设置key, 减少类似将最后一个节点移动到列表首部的操作 来进行优化
Diff 优化
- 减少 update 次数, 减少非理想状况的
setState() - 减少跨层级移动节点, 尽量平行移动
- 使用合适的 key
forceUpdate 调用后将会直接进入 componentWillUpdate 阶段,无法拦截,因此在实际项目中应该弃用。
BatchedUpdates 批量更新
可以说,setState 是对单个组件的合并渲染,batchedUpdates 是对多个组件的合并渲染。合并渲染是 React 最主要的优化手段。
React patch, Event System 任务系统
updateFiberAndView 是位于一个 requestIdleCallback 中,因此它的时间很有限,分给 DFS 部分的时间也更少,因此它们不能做太多事情。这怎么办呢,标记一下,留给 commit 阶段做。于是产生了一个任务系统。
每个 Fiber 分配到新的任务时,就通过位操作,累加一个 sideEffect。sideEffect 字面上是副作用的意思,非常重 FP 流的味道,但我们理解为任务更方便我们的理解。
每个 Fiber 可能有多个任务,比如它要插入 DOM 或移动,就需要加上 Replacement,需要设置样式,需要加上 Update。
怎么添加任务呢?
fiber.effectTag |= Update
怎么保证不会重复添加相同的任务?
fiber.effectTag &= ~DidCapture
在 commit 阶段,确保其包含了某项任务, 相同性质任务只执行一次, 也可用素数乘除实现
if (fiber.effectTag & Update) {
/*操作属性*/
}
任务参考 TypeOfSideEffect
Fiber
Fiber 代表一种工作量单位 (unit of work) / 时间切片 (time slicing).
A Fiber is work on a Component that needs to be done or was done. There can be more than one (but at most two, current and alternate) per component. (Component._reactInternalFiber) current fiber will be replaced by alternate after update
关键属性 (省略部分 i)
type Fiber = {
// 双向链表结构
tag: TypeOfWork
key: null | string // Unique identifier of this child.
type: any // The function/class/module associated with this fiber
stateNode: any // local state associated with the fiber
/* the Fiber that the result of this fiber process should be merged to */
return: Fiber | null // parent node
child: Fiber | null // first child node
sibling: Fiber | null // sibling node
// Input is the data coming into process this fiber. Arguments. Props.
pendingProps: any // This type will be more specific once we overload the tag.
memoizedProps: any // The props used to create the output.
// A queue of state updates and callbacks.
updateQueue: UpdateQueue<any> | null
memoizedState: any // The state used to create the output
// Effect
effectTag: TypeOfSideEffect
nextEffect: Fiber | null // next node in singly linked list of effects
firstEffect: Fiber | null
lastEffect: Fiber | null // head & tail fiber with side-effect within this subtree
alternate: Fiber | null // pooled version of a fiber
mode: TypeOfMode
// A linked-list of contexts that this fiber depends on
firstContextDependency: ContextDependency<mixed> | null
}
enum TypeOfWork {
IndeterminateComponent = 0, // Before we know whether it is functional or class
FunctionalComponent = 1,
ClassComponent = 2, // inherit from React Component
HostRoot = 3, // Root of a host tree by ReactDOM/ReactNative.render().
HostPortal = 4, // A subtree. Could be an entry point to a different renderer.
HostComponent = 5, // injected by host environment, e.g. DOM in browser
HostText = 6,
CoroutineComponent = 7,
CoroutineHandlerPhase = 8,
YieldComponent = 9,
Fragment = 10,
Mode = 11
}
// TypeOfSideEffect
export const NoEffect = /* */ 0b00000000000
export const PerformedWork = /* */ 0b00000000001
// You can change the rest (and add more).
export const Placement = /* */ 0b00000000010
export const Update = /* */ 0b00000000100
export const PlacementAndUpdate = /* */ 0b00000000110
export const Deletion = /* */ 0b00000001000
export const ContentReset = /* */ 0b00000010000
export const Callback = /* */ 0b00000100000
export const DidCapture = /* */ 0b00001000000
export const Ref = /* */ 0b00010000000
export const Snapshot = /* */ 0b00100000000
// Update & Callback & Ref & Snapshot
export const LifecycleEffectMask = /* */ 0b00110100100
// Union of all host effects
export const HostEffectMask = /* */ 0b00111111111
export const Incomplete = /* */ 0b01000000000
export const ShouldCapture = /* */ 0b10000000000
enum Priority {
NoWork = 0, // No work is pending.
SynchronousPriority = 1, // For controlled text inputs. Synchronous side-effects.
TaskPriority = 2, // including animation (by requestAnimationFrame), Completes at the end of the current tick.
HighPriority = 3, // completed by requestIdleCallback, Interaction that needs to complete pretty soon to feel responsive
LowPriority = 4, // can be delayed, such as data fetching, or result from updating stores.
OffscreenPriority = 5 // Won't be visible but do the work in case it becomes visible.
}
特点
- 把未完成的工作中可中断的任务拆分, Cooperative scheduling
- 对正在做的工作确定并根据情况变化调整优先级
- 复用已完成的单位, 或重做
- 丢弃不需要再做的任务
- 增量渲染, 可控更新
- 父子任务间切换
- 不同类型的更新有优先级
- 并发
Reconciliation & Render
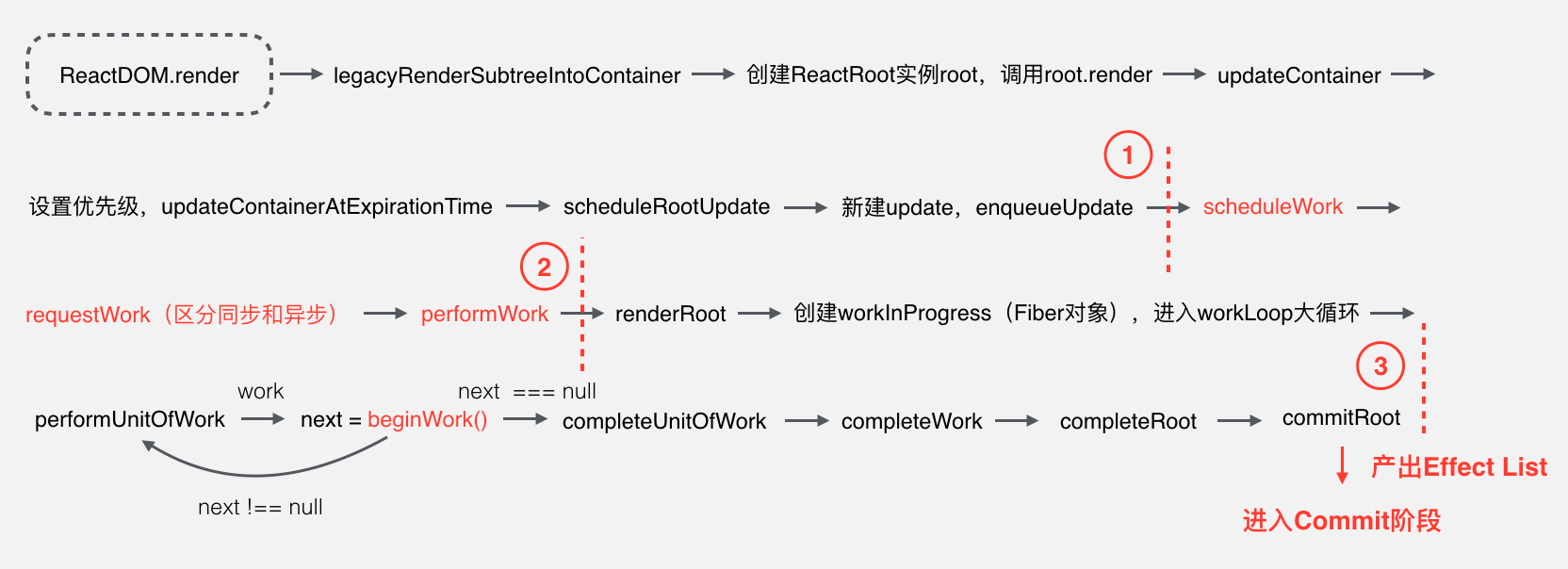
以下为引用内容
把渲染更新过程拆分成多个子任务,每次只做一小部分,做完看是否还有剩余时间,如果有继续下一个任务;如果没有,挂起当前任务,将时间控制权交给主线程,等主线程不忙的时候在继续执行。 这种策略叫做 Cooperative Scheduling(合作式调度),操作系统常用任务调度策略之一。
合作式调度主要就是用来分配任务的,当有更新任务来的时候,不会马上去做 Diff 操作,而是先把当前的更新送入一个 Update Queue 中,然后交给 Scheduler 去处理,Scheduler 会根据当前主线程的使用情况去处理这次 Update。
为了实现这种特性,使用了 requestIdleCallback API。对于不支持这个 API 的浏览器,用 ReactScheduler
在上面我们已经知道浏览器是一帧一帧执行的,在两个执行帧之间,主线程通常会有一小段空闲时间,requestIdleCallback 可以在这个空闲期(Idle Period)调用空闲期回调(Idle Callback),执行一些任务。
- 低优先级任务由 requestIdleCallback 处理;
- 高优先级任务,如动画相关的由 requestAnimationFrame 处理;
- requestIdleCallback 可以在多个空闲期调用空闲期回调,执行任务;
- requestIdleCallback 方法提供 deadline,即任务执行限制时间,以切分任务,避免长时间执行,阻塞 UI 渲染而导致掉帧;
这个方案看似确实不错,但是怎么实现可能会遇到几个问题:
- 如何拆分成子任务?
- 一个子任务多大合适?
- 怎么判断是否还有剩余时间?
- 有剩余时间怎么去调度应该执行哪一个任务?
- 没有剩余时间之前的任务怎么办?
接下里整个 Fiber 架构就是来解决这些问题的。
react 本身为了提高页面渲染性能,推出了一些最佳实践
- vdom 减少对 dom 的直接操作
- 无状态组件 减少组件内部状态和复杂度
- shouldComponentUpdate 减少 diff 的次数
- immutable 减少 diff 的成本
补充
操作系统常用任务调度策略:先来先服务(FCFS)调度算法、短作业(进程)优先调度算法(SJ/PF)、最高优先权优先调度算法(FPF)、高响应比优先调度算法(HRN)、时间片轮转法(RR)、多级队列反馈法。
React runtime instances
- DOM
- Elements
- Instances (generate from elements, fiber tree inside)
- fiber tree (current context)
- workInProgress tree (temp, snapshot to be updated)
- effect list (temp, merged side effect list from workInProgress)
HTML 转义
React 会将所有要显示到 DOM 的字符串转义,防止 XSS。所以,如果 JSX 中含有转义后的 实体字符,比如 ©(©),则最后 DOM 中不会正确显示,因为 React 自动把 © 中的特 殊字符转义了。有几种解决办法:
- 直接使用 UTF-8 字符 ©;
- 使用对应字符的 Unicode 编码查询编码;
- 使用数组组装
<div>{['cc ', <span>©</span>, ' 2015']}</div>; - 直接插入原始的 HTML。
此外,React 提供了 dangerouslySetInnerHTML 属性。正如其名,它的作用就是避免 React 转 义字符,在确定必要的情况下可以使用它:
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: "cc © 2015" }} />
Hooks
useState 实现原理
当调用 useState 的时候,会返回形如 (变量, 函数) 的一个 元祖。并且 state 的初始值就是外部调用 useState 的时候,传入的参数。
useState 返回的用于更改状态的函数,自动调用了 render 方法来触发视图更新。
const states: any[] = [] // 全局 array
let cursor: number = 0 // 全局计数器,每次 render 重置
function useState<T>(initialState: T): [T, (newState: T) => void] {
const currenCursor = cursor
states[currenCursor] = states[currenCursor] || initialState // 检查是否渲染过
function setState(newState: T) {
states[currenCursor] = newState
render() // ReactDOM.render
}
++cursor // update: cursor
return [states[currenCursor], setState]
}
状态保存在一个全局容器 Array 对象中。
第一次渲染时候,根据
useState顺序,逐个声明 state 并且将其放入全局Array中。每次声明state,都要将cursor(全局计数变量) 增加 1。更新 state,触发再次渲染的时候,
cursor被重置为 0。按照useState的声明顺序,依次拿出最新的 state 的值,视图更新。
因此不能在循环/判断等非函数组件顶级 scope 处使用,因为其顺序不可控。
useEffect 原理
useEffect 作用是 在指定依赖数组后,如果下次渲染时,数组中的元素没变,那么就不会触发这个副作用(可以类比 Class 类的关于 nextprops 和 prevProps 的生命周期)。好处显然易见,相比于直接裸写在函数组件顶层,useEffect 能根据需要,避免多余的 render。
一个不包括销毁副作用功能的 useEffect
// 还是利用 Array + Cursor的思路
const allDeps: any[][] = []
let effectCursor: number = 0
function useEffect(callback: () => void, deps: any[]) {
if (!allDeps[effectCursor]) {
// 初次渲染:赋值 + 调用回调函数
allDeps[effectCursor] = deps
++effectCursor
callback()
return
}
const currenEffectCursor = effectCursor
const rawDeps = allDeps[currenEffectCursor]
// 检测依赖项是否发生变化,发生变化需要重新render
const isChanged = rawDeps.some(
(dep: any, index: number) => dep !== deps[index]
)
if (isChanged) {
callback()
}
++effectCursor
}
function render() {
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"))
effectCursor = 0 // 注意将 effectCursor 重置为0
}
Class vs Hooks (todo)
Class 代码逻辑清晰(构造函数、componentDidMount 等), 不易内存泄漏
useCallback
快照 vs 最新值
rerender 机制
class 重渲染触发条件,此处暂时不考虑采用 shouldComponentUpdate 和 pureComponent 优化
this.setState: 无条件重渲染,不进行新旧比较this.forceUpdate: 无条件重渲染,不进行新旧比较- 父组件
render带动子组件render:无条件,和props是否更新无关 - 祖先组件
context变动: 不做props变动假设
我们发现 react 默认的重渲染机制压根没有对 props 做任何假设,性能优化完全交给框架去做,react-redux 基于 shouldComponentUpdate, mobx-react 基于 this.forceUpdatehooks 来做一些性能优化
即使不用 hooks 本身 functional 组件和 class 组件表现就存在较大差异,由于 hook 目前只能在 function 组件里使用,这导致了一些本来是 functional 组件编程思维的问题反映到了 hooks 上。
hooks 的使用引入了两条强假设,导致了编程思维的巨大变动
只能在 functional 组件里使用: 导致我们需要处理最新值的问题
副作用(包括 rerender 和 effect)基于新旧值的 reference equality: 强制我们使用 immutable 进行编程
上述两条带来了很大的心智负担
Suspence (todo)
Performance
Profiler
16.5+, 录制检测
Q & A
Key points:
<ErrorBoundary>:
hooks: 允许在不编写类的情况下使用 state 和其他 React 特性, 减少层级嵌套或重写。使用 Hooks,可以从组件中提取有状态逻辑,这样就可以独立地测试和重用它。Hooks 允许在不改变组件层次结构的情况下重用有状态逻辑,这样在许多组件之间或与社区共享 Hooks 变得很容易。
<StrictMode>: 验证内部组件是否遵循某些推荐做法,如果没有,会在控制台给出警告。
验证是否使用的已经废弃的方法,如果有,会在控制台给出警告。
通过识别潜在的风险预防一些副作用。
prop drilling: prop 层层传递, 可以用 React.Context 或 状态管理库 代替
Fiber: 新的协调引擎或重新实现核心算法。它的主要目标是支持虚拟 DOM 的增量渲染 (能够将渲染工作分割成块,并将其分散到多个帧中)。React Fiber 的目标是提高其在动画、布局、手势、暂停、中止或重用等方面的适用性,并为不同类型的更新分配优先级,以及新的并发原语。
Q: redux 问题 参考掘金
A: redux 本身有哪些作用?我们先来快速的过一下 redux 的核心思想(工作流程):
createStore.js: 将状态统一放在一个 state 中,由 store 来管理这个 state。combineReducers.js: 这个 store 按照 reducer 的 "shape"(形状)创建。reducer 的作用是接收到 action 后,输出一个新的状态,对应地更新 store 上的状态。dispatch(): 根据 redux 的原则指导,外部改变 state 的最佳方式是通过调用 store 的 dispatch 方法,触发一个 action,这个 action 被对应的 reducer 处理,完成 state 更新。subscribe(),getState()å: 可以通过 subscribe 在 store 上添加一个监听函数。每当调用 dispatch 方法时,会执行所有的监听函数。applyMiddleware(), 可以添加中间件(中间件是干什么的我们后面讲)处理副作用。compose.js,bindActionCreators,hs: 工具函数